FSM: - FSM Stands for Finite State Machine. A finite state machine
with a sequential circuit with “random” next state logic. An FSM consists of two blocks of combinational
logic — Next state logic and output
logic.
A
FSM is specified by five entities: symbolic state, input signals, output
signals, next state function and output function. The FSM transits from one
state to another. The new state is determined by next state function, which is
a function of next state and input signals.
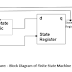
The block diagram of FSM is similar to
regular sequential circuit. The state register is memory element that store the
state of FSM. It is synchronized by a global clock. The next state logic implements
the next state function. The output logic implements the output function. The
diagram includes both moore output logic. Whose input is the next state.
FSM
can be used to detecting the unique pattern from an input data stream or
generating a specific sequence of output values.
• Finite String Pattern Recognizer
•
Traffic Light Controller
There are two general classes of finite
state machine, characterized by their functional specifications.
1.
In
Moore machine, the outputs depend
only on the current state of the machine.
2.
In
Mealy machine, the output depends on
both the current state and the current inputs.
Finite state machines provide a
systematic way to design synchronous sequential circuits given a functional
specification.
(Figure: Moore machine and Mealy machine)
FSM
Advantages: -
·
Simple
·
Predictable ( deterministic FSM ) - given a set
of inputs and a known current state, the state transition can be predicted,
allowing for easy testing.
·
Due to their simplicity, FSMs are quick to
design, quick to implement and quick in execution.
·
Easy to transfer from a meaningful abstract
representation to a coded implementation.
·
FSM
is an old knowledge representation and system modeling technique.
FSM
Disadvantages: -
·
The conditions for state transitions are
ridged, meaning they are fixed.
·
The
predictable nature of deterministic FSMs can be unwanted in some domains such
as computer games.
·
Not
suited to all problem domains.
















simple and easy
ReplyDelete:)