Color Image processing
The use of color in image processing is motivated by two
principal factors. First, color is a powerful descriptor that often simplifies
object identification and extraction from a scene. Second, human can discern
thousands of color shades and intensities, compared to about only two dozen
shades of grat. This factor is particularly important in manual image analysis.
In the first category, the image in question typically are
acquired with full color sensor, such as color TV camera or color scanner. In
the second category, the problem is one of assigning a color to particular
monochrome intensity or range of intensities.
Full color image processing techniques are now used in a
broad range of applications, including publishing, visualization, and the
internet.
Color images processing is divided into two major areas: -
full color image processing and pseudocolor image processing.
Three basic quantities are used to describe the quality of
a chromatic light source is:
1. Radiance
2. Luminance
3. Brightness
Radiance is
the total amount of energy that flows from the light source, and it is usually
measured in watt (W).
Luminance is measured in terms of lumens (lm), gives the measure of
the amount of energy an observer perceives from a light source.
Brightness
is
a subjective descriptor that is practically impossible to measure.
Primary
colors: - Red (R), Green (G) and Blue (B).
Secondary
colors: - Magenta (red + blue), Cyan (green + blue), Yellow (red +
green).
The characteristics generally used to distinguish one color
from another are brightness, hue and saturation. Hue and saturation taken
together are called chromaticity.
And therefore a color may be characterized by its brightness and chromaticity.
Color
Models: - Basically, the colors that humans and some other animals perceive
in an object are determined by the nature of the light reflected from the
object. Characterization of light is central to the science of color. If the
light is achromatic (void of color), its only attribute is its intensity, or
amount. Achromatic light is what viewers see on a black and white television
set.
·
RGB (red, green, blue) Model
·
CMY (cyan, magenta, yellow) Model
·
CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, black) Model
·
HSI (hue, saturation, intensity) Model
RGB
Model: - In RGB
model, each color appears in its primary spectral components of red, green and
blue. This model is based on Cartesian coordinate system. Image represented in
RGB color model consist of three components images.
The number of bits used to represent each pixel in RGB
space is called the pixel depth. The
total number of colors in 24-bit RGB image is 2^24 = 14,777,216.
The term full color image
is used often to denote 24-bit RGB color image.
The
CMY Color Model: - Cyan, magenta and yellow are the secondary
color of light or alternatively primary colors of pigments. For example, when a
surface is coated with cyan pigment is illuminated with white light, no red
light is reflected from surface. This is cyan reflects red light from reflected
white light. Which itself is composed of equal amount of red, green and blue
light.
The HIS Model: - Createing colos in RGB and CMY
models and changing from one model to another is strainghtforward process.
These color systems are ideally suited for hardware systems. When human views a
object, we describe it by its hue and saturations.
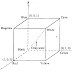
(Figure: Conceptual relationship between RGB and HSI models)
The key point
to keep in mind regarding the cube arrangment and its corresponding HIS color
space is that HSI space is represented by a vertical intensity axis and locus
of color point that lies on plan perpendicular to this axis.


















simple and easy :)
ReplyDelete